GitSwarm-EE 2017.1-1 Documentation
Integrate your GitSwarm server with Bitbucket
Import projects from Bitbucket.org and login to your GitSwarm instance with your Bitbucket.org account.
Overview
You can set up Bitbucket.org as an OAuth provider so that you can use your credentials to authenticate into GitSwarm or import your projects from Bitbucket.org.
- To use Bitbucket.org as an OmniAuth provider, follow the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider section.
- To import projects from Bitbucket, follow both the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider and Bitbucket project import sections.
Bitbucket OmniAuth provider
Note: Make sure to first follow the Initial OmniAuth configuration before proceeding with setting up the Bitbucket integration.
To enable the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider you must register your application with Bitbucket.org. Bitbucket will generate an application ID and secret key for you to use.
- Sign in to Bitbucket.org.
- Navigate to your individual user settings (Bitbucket settings) or a team's settings (Manage team), depending on how you want the application registered. It does not matter if the application is registered as an individual or a team, that is entirely up to you.
- Select OAuth in the left menu under "Access Management".
- Select Add consumer.
Provide the required details:
Item Description Name This can be anything. Consider something like <Organization>'s GitSwarmor<Your Name>'s GitSwarmor something else descriptive.Application description Fill this in if you wish. Callback URL Leave blank. URL The URL to your GitLab installation, e.g., https://gitswarm.example.com.And grant at least the following permissions:
Account: Email Repositories: Read, AdminNote: It may seem a little odd to giving GitSwarm admin permissions to repositories, but this is needed in order for GitSwarm to be able to clone the repositories.
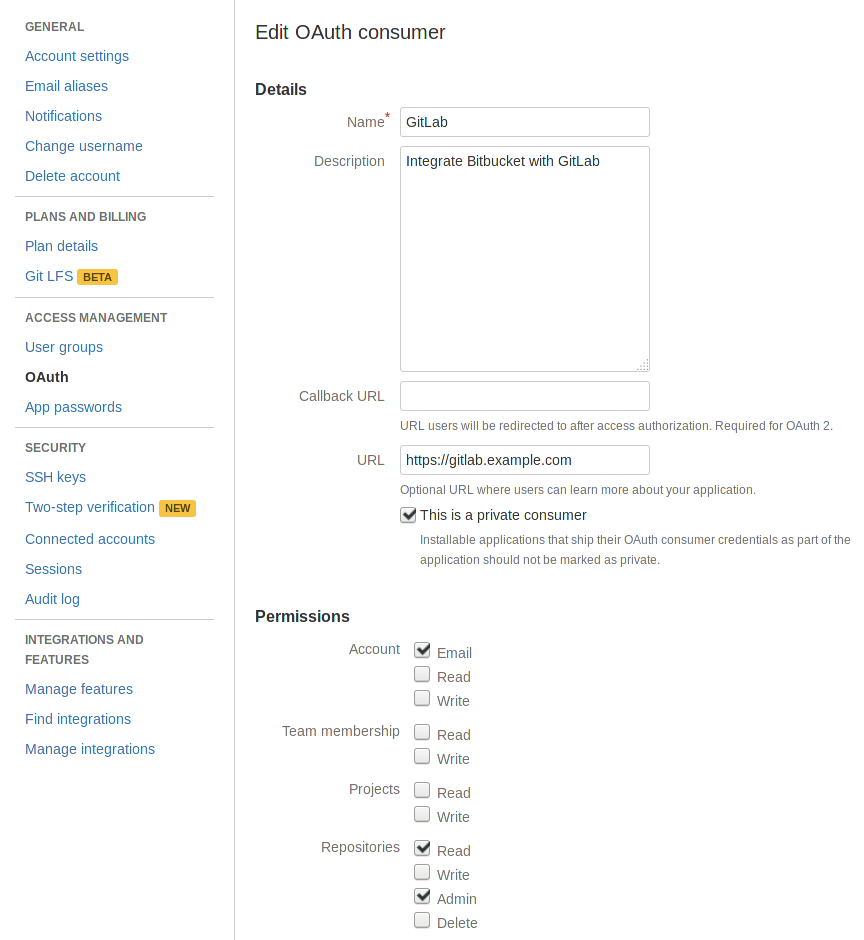
- Select Save.
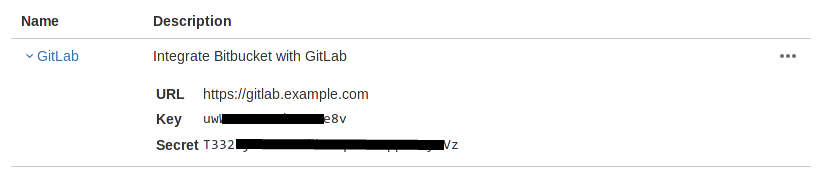
Select your newly created OAuth consumer and you should now see a Key and Secret in the list of OAuth customers. Keep this page open as you continue the configuration.
On your GitSwarm server, open the configuration file:
# For package installations sudo editor /etc/gitswarm/gitswarm.rb # For source installations sudo -u git -H editor /home/git/gitlab/config/gitlab.yml- Follow the Initial OmniAuth Configuration for initial settings.
Add the Bitbucket provider configuration:
For package installations:
gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [ { "name" => "bitbucket", "app_id" => "BITBUCKET_APP_KEY", "app_secret" => "BITBUCKET_APP_SECRET", "url" => "https://bitbucket.org/" } ]For source installations:
- { name: 'bitbucket', app_id: 'BITBUCKET_APP_KEY', app_secret: 'BITBUCKET_APP_SECRET' }
Where
BITBUCKET_APP_KEYis the Key andBITBUCKET_APP_SECRETthe Secret from the Bitbucket application page.- Save the configuration file.
Reconfigure or restart GitSwarm for the changes to take effect if you installed GitSwarm via Omnibus or from source respectively.
On the sign in page there should now be a Bitbucket icon below the regular sign in form. Click the icon to begin the authentication process. Bitbucket will ask the user to sign in and authorize the GitSwarm application. If everything goes well, the user will be returned to GitSwarm and will be signed in.
Bitbucket project import
To allow projects to be imported directly into GitSwarm, Bitbucket requires two extra setup steps compared to GitHub and GitLab.com.
Bitbucket doesn't allow OAuth applications to clone repositories over HTTPS, and instead requires GitSwarm to use SSH and identify itself using your GitSwarm server's SSH key.
To be able to access repositories on Bitbucket, GitSwarm will automatically register your public key with Bitbucket as a deploy key for the repositories to be imported. Your public key needs to be at ~/.ssh/bitbucket_rsa which translates to /var/opt/gitswarm/.ssh/bitbucket_rsa for package installations and to /home/git/.ssh/bitbucket_rsa.pub for source installations.
Below are the steps that will allow GitSwarm to be able to import your projects from Bitbucket.
- Make sure you have enabled the Bitbucket OAuth support.
Create a new SSH key with an empty passphrase:
sudo -u git -H ssh-keygenWhen asked to 'Enter file in which to save the key' enter:
/var/opt/gitswarm/.ssh/bitbucket_rsafor package installations or/home/git/.ssh/bitbucket_rsafor source installations. The name is important so make sure to get it right.Warning: This key must NOT be associated with ANY existing Bitbucket accounts. If it is, the import will fail with an
Access denied! Please verify you can add deploy keys to this repository.error.Next, you need to to configure the SSH client to use your new key. Open the SSH configuration file of the
gituser:# For package installations sudo editor /var/opt/gitswarm/.ssh/config # For source installations sudo editor /home/git/.ssh/configAdd a host configuration for
bitbucket.org:Host bitbucket.org IdentityFile ~/.ssh/bitbucket_rsa User git- Save the file and exit.
Manually connect to
bitbucket.orgover SSH, while logged in as thegituser that GitSwarm will use:sudo -u git -H ssh bitbucket.orgThat step is performed because GitSwarm needs to connect to Bitbucket over SSH, in order to add
bitbucket.orgto your GitSwarm server's known SSH hosts.Verify the RSA key fingerprint you'll see in the response matches the one in the Bitbucket documentation (the specific IP address doesn't matter):
The authenticity of host 'bitbucket.org (104.192.143.1)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:zzXQOXSRBEiUtuE8AikJYKwbHaxvSc0ojez9YXaGp1A. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?- If the fingerprint matches, type
yesto continue connecting and havebitbucket.orgbe added to your known SSH hosts. After confirming you should see a permission denied message. If you see an authentication successful message you have done something wrong. The key you are using has already been added to a Bitbucket account and will cause the import script to fail. Ensure the key you are using CANNOT authenticate with Bitbucket. Restart GitSwarm to allow it to find the new public key.
Your GitSwarm server is now able to connect to Bitbucket over SSH. You should be able to see the "Import projects from Bitbucket" option on the New Project page enabled.
Acknowledgemts
Special thanks to the writer behind the following article: